Difference between revisions of "Stormwater planters"
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) m |
|||
| (39 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
<imagemap> | <imagemap> | ||
Image:Stormwater planter.png|thumb|700 px|This is an image map of a stormwater planter, clicking on components will load the appropriate article. | Image:Stormwater planter.png|thumb|700 px|This is an image map of a stormwater planter, clicking on components will load the appropriate article. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 9: | ||
rect 480 400 534 517 [[Forebays]] | rect 480 400 534 517 [[Forebays]] | ||
circle 190 169 26 [[Overflow]] | circle 190 169 26 [[Overflow]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
rect 152 1166 340 1189 [[mulch]] | rect 152 1166 340 1189 [[mulch]] | ||
rect 65 1164 538 1190 [[mulch]] | rect 65 1164 538 1190 [[mulch]] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 20: | ||
poly 139 1158 149 1155 151 1303 352 1343 542 1305 541 1165 550 1161 553 1311 354 1355 139 1311 [[Liner]] | poly 139 1158 149 1155 151 1303 352 1343 542 1305 541 1165 550 1161 553 1311 354 1355 139 1311 [[Liner]] | ||
</imagemap> | </imagemap> | ||
| − | + | [[File:Stormwater planter pu.png|thumb|An above ground planter with downspout and overflow illustrated.]] | |
| − | Over | + | Over underground infrastructure, soils prone to subsidence, or on sites considered to be pollution hot spots, it may be necessary to prevent all [[infiltration]]. Stormwater planters are "filtration-only" BMPs, similar to bioretention cells, that can be squeezed into tight urban spaces, adjacent to buildings and within the usual setbacks required for infiltrating facilities. Stormwater planters can also be used as a means of providing building-integrated LID by capturing a portion of the rainwater from the rooftop. |
This type of cell can be constructed above grade in any waterproof and structurally sound container, e.g. in cast concrete or a metal tank. | This type of cell can be constructed above grade in any waterproof and structurally sound container, e.g. in cast concrete or a metal tank. | ||
| − | + | {{TOClimit|2}} | |
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
{{textbox|Stormwater planters are an ideal technology for: | {{textbox|Stormwater planters are an ideal technology for: | ||
| Line 33: | Line 29: | ||
*Zero-lot-line developments such as condos or dense urban infill.}} | *Zero-lot-line developments such as condos or dense urban infill.}} | ||
'''The fundamental components of a stormwater planter are:''' | '''The fundamental components of a stormwater planter are:''' | ||
| − | *a planting bed of [[ | + | *a planting bed of [[Filter media| filter media]], |
| − | *suitable vegetation, | + | *suitable [[Plant lists| vegetation]], |
*decorative aggregate or [[stone]], | *decorative aggregate or [[stone]], | ||
| − | *An [[underdrain]] | + | *An [[underdrain]], |
| + | *An impermeable [[liner]], | ||
'''The design may benefit from:''' | '''The design may benefit from:''' | ||
| − | *A [[level spreaders| level spreader]] | + | *A [[level spreaders| level spreader]] |
==Planning Considerations== | ==Planning Considerations== | ||
| + | Stormwater planters may be integrated into the landscape similarly to bioretention practices. See [[Bioretention#Planning considerations|bioretention planning]]. | ||
| + | ===Additional site opportunities=== | ||
| + | As they do not require connection to the earth for infiltration purposes, stormwater planters can also be used in elevated locations. They are sometimes used in retrofit applications on otherwise impermeable surface, as raised beds or planters surrounding buildings. They can be employed to capture runoff from [[downspout disconnection| roof drains or downspouts]] or even upon terraces or vertical surfaces of buildings. | ||
==Design== | ==Design== | ||
| − | {{:Planters:Sizing}} | + | {{:Planters: Sizing}} |
| − | === | + | ===Filter media=== |
| − | [[ | + | See [[Bioretention: Filter media]] |
===Underdrain=== | ===Underdrain=== | ||
| − | Stormwater planters differ | + | Stormwater planters differ from full and/or partial infiltration [[bioretention]] practices in that the storage function is provided only by the [[water retention capacity]] of the [[filter media]]. As such, there is no storage reservoir and the only purpose to the aggregate layer is to drain water to the perforated [[pipe]]. For this, a medium aggregate as described in [[choker layer]] is recommended as it negates the need for a separating layer to the filter media. Design details can be found here [[Underdrains#Underdrains for non-exfiltrating practices|Underdrains]] for non-exfiltrationg practices. |
| − | [[Underdrains#Underdrains for non-exfiltrating practices| | ||
===Planting=== | ===Planting=== | ||
| − | Stormwater planters routinely capture only rainwater flowing from adjacent rooftops. This means that [[salt]] may be less of a concern than in [[Bioretention: Parking lots]] or [[Bioretention: Streetscapes]]. | + | *Planters must be designed in a way that insulates the soil through freezing temperatures, or plant species that can survive the winter season in raised planters must be used. |
| − | The [[plant lists]] are still a good place to start when selecting species for LID in Ontario. | + | *Stormwater planters routinely capture only rainwater flowing from adjacent rooftops. This means that [[salt]] may be less of a concern than in [[Bioretention: Parking lots]] or [[Bioretention: Streetscapes]]. |
| + | *The [[plant lists]] are still a good place to start when selecting species for LID in Ontario. | ||
| + | *A more formal aesthetic for the planting design is appropriate for the urban hardscape setting. | ||
===Liners=== | ===Liners=== | ||
{{:Liner}} | {{:Liner}} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Filter bed surface== |
| − | As stormwater planters are often quite small and receive very rapid flow, both a [[level spreader]] and the use of | + | As stormwater planters are often quite small and receive very rapid flow, both a [[level spreader]] and the use of mulch and stone to dissipate energy from concentrated inflow are strongly recommended. |
==Gallery== | ==Gallery== | ||
| Line 66: | Line 67: | ||
==Performance== | ==Performance== | ||
| − | + | ===Hydrology=== | |
| − | Water quality <ref>Macnamara, J.; Derry, C. Pollution Removal Performance of Laboratory Simulations of Sydney’s Street Stormwater Biofilters. Water 2017, 9, 907.;doi:10.3390/w9110907</ref> | + | |
| + | <ref>Davis, Allen P., Robert G. Traver, William F. Hunt, Ryan Lee, Robert A. Brown, and Jennifer M. Olszewski. “Hydrologic Performance of Bioretention Storm-Water Control Measures.” Journal of Hydrologic Engineering 17, no. 5 (May 2012): 604–14. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000467.</ref> | ||
| + | <ref>Yeakley, J.A., and K.K. Norton. “Performance Assessment of Three Types of Rainwater Detention Structures for an Urban Development in Wilsonville, Oregon, USA,” 70. Portland, 2009.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Water quality=== | ||
| + | <ref>Macnamara, J.; Derry, C. Pollution Removal Performance of Laboratory Simulations of Sydney’s Street Stormwater Biofilters. Water 2017, 9, 907.;doi:10.3390/w9110907</ref> | ||
<ref>Lucke, T., & Nichols, P. W. B. (2015). The pollution removal and stormwater reduction performance of street-side bioretention basins after ten years in operation. Science of The Total Environment, 536, 784–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2015.07.142</ref> | <ref>Lucke, T., & Nichols, P. W. B. (2015). The pollution removal and stormwater reduction performance of street-side bioretention basins after ten years in operation. Science of The Total Environment, 536, 784–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2015.07.142</ref> | ||
<ref>Macnamara, J.; Derry, C. Pollution Removal Performance of Laboratory Simulations of Sydney’s Street Stormwater Biofilters. Water 2017, 9, 907. doi:10.3390/w9110907</ref> | <ref>Macnamara, J.; Derry, C. Pollution Removal Performance of Laboratory Simulations of Sydney’s Street Stormwater Biofilters. Water 2017, 9, 907. doi:10.3390/w9110907</ref> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:27, 23 July 2020
Over underground infrastructure, soils prone to subsidence, or on sites considered to be pollution hot spots, it may be necessary to prevent all infiltration. Stormwater planters are "filtration-only" BMPs, similar to bioretention cells, that can be squeezed into tight urban spaces, adjacent to buildings and within the usual setbacks required for infiltrating facilities. Stormwater planters can also be used as a means of providing building-integrated LID by capturing a portion of the rainwater from the rooftop. This type of cell can be constructed above grade in any waterproof and structurally sound container, e.g. in cast concrete or a metal tank.
Overview[edit]
Stormwater planters are an ideal technology for:
- Sites which cannot infiltrate water owing to contaminated soils or shallow bedrock,
- Zero-lot-line developments such as condos or dense urban infill.
The fundamental components of a stormwater planter are:
- a planting bed of filter media,
- suitable vegetation,
- decorative aggregate or stone,
- An underdrain,
- An impermeable liner,
The design may benefit from:
Planning Considerations[edit]
Stormwater planters may be integrated into the landscape similarly to bioretention practices. See bioretention planning.
Additional site opportunities[edit]
As they do not require connection to the earth for infiltration purposes, stormwater planters can also be used in elevated locations. They are sometimes used in retrofit applications on otherwise impermeable surface, as raised beds or planters surrounding buildings. They can be employed to capture runoff from roof drains or downspouts or even upon terraces or vertical surfaces of buildings.
Design[edit]
This article is specific to flow-through stormwater planters, vegetated systems that do not infiltrate water to the native soil.
If you are designing a planted system which does infiltrate water, see advice on Bioretention: Sizing.
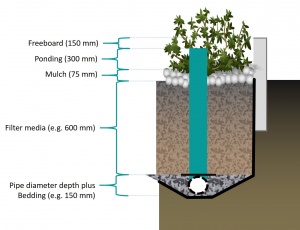
The dimensions of a stormwater planter are largely predetermined according to the function of the component. As they do not contain a storage reservoir the planters rely more upon careful selection of materials. Both the filter media and the perforations of the pipe play critical roles for flow control.
| Component | Recommended depth (with underdrain pipe) | Typical porosity (n) |
|---|---|---|
| Ponding (dp) | 150 to 450 mm | 1 |
| Mulch | 75 ± 25 mm |
|
| Filter media (dm) |
|
|
| Pipe diameter reservoir | Is equal to underdrain pipe diameter | 0.4 |
| Pipe bedding (db) | 50 mm (although commonly omitted altogether). | 0.4 |
Filter media[edit]
See Bioretention: Filter media
Underdrain[edit]
Stormwater planters differ from full and/or partial infiltration bioretention practices in that the storage function is provided only by the water retention capacity of the filter media. As such, there is no storage reservoir and the only purpose to the aggregate layer is to drain water to the perforated pipe. For this, a medium aggregate as described in choker layer is recommended as it negates the need for a separating layer to the filter media. Design details can be found here Underdrains for non-exfiltrationg practices.
Planting[edit]
- Planters must be designed in a way that insulates the soil through freezing temperatures, or plant species that can survive the winter season in raised planters must be used.
- Stormwater planters routinely capture only rainwater flowing from adjacent rooftops. This means that salt may be less of a concern than in Bioretention: Parking lots or Bioretention: Streetscapes.
- The plant lists are still a good place to start when selecting species for LID in Ontario.
- A more formal aesthetic for the planting design is appropriate for the urban hardscape setting.
Liners[edit]
A liner is sometime incorporated into non-infiltrating practices such as stormwater planters, or has also been applied in permeable pavements installations where seperation from the native soils and groundwater was required.
- Waterproof containment can be created using a plastic membrane/liner (HDPE or EPDM are common materials).
- When the membrane is being used directly in the ground, punctures from stones can be prevented by compacting a layer sand (30 - 50 mm) over the soil prior to installing the membrane.
- Alternatively, a manufactured cushion fabric (geotextile) can be employed for this purpose.
- The top surface of the membrane must also be protected from stone and gravel being used for inside the BMP. Again, sand or a cushion fabric may be used.
- When a pipe is used to provide drainage from the BMP cell, a 'pipe boot' should be sealed to both the pipe and the liner to prevent leaks.
Filter bed surface[edit]
As stormwater planters are often quite small and receive very rapid flow, both a level spreader and the use of mulch and stone to dissipate energy from concentrated inflow are strongly recommended.
Gallery[edit]
Stormwater planters are ideal for situating alongside buildings to capture rainwater from roof runoff. LSRCA headquarters, 2017.
Stormwater planter, treating downspout runoff, at Waterview Rec Center, Philidelphia
Photo credit: PWDRain garden, Illick Hall, SUNY College of Environmental Science and Forestry, Syracuse, NY
Photo credit: DASonnenfeld
Performance[edit]
Hydrology[edit]
Water quality[edit]
See Also[edit]
Proprietary links[edit]
A number of precast modules exist to contain treatment media. As many of these systems are enclosed water balance calculations may be erroneous where evapotranspiration is constrained.
In our effort to make this guide as functional as possible, we have decided to include proprietary systems and links to manufacturers websites.
Inclusion of such links does not constitute endorsement by the Sustainable Technologies Evaluation Program.
Lists are ordered alphabetically; link updates are welcomed using the form below.
- ↑ Davis, Allen P., Robert G. Traver, William F. Hunt, Ryan Lee, Robert A. Brown, and Jennifer M. Olszewski. “Hydrologic Performance of Bioretention Storm-Water Control Measures.” Journal of Hydrologic Engineering 17, no. 5 (May 2012): 604–14. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000467.
- ↑ Yeakley, J.A., and K.K. Norton. “Performance Assessment of Three Types of Rainwater Detention Structures for an Urban Development in Wilsonville, Oregon, USA,” 70. Portland, 2009.
- ↑ Macnamara, J.; Derry, C. Pollution Removal Performance of Laboratory Simulations of Sydney’s Street Stormwater Biofilters. Water 2017, 9, 907.;doi:10.3390/w9110907
- ↑ Lucke, T., & Nichols, P. W. B. (2015). The pollution removal and stormwater reduction performance of street-side bioretention basins after ten years in operation. Science of The Total Environment, 536, 784–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2015.07.142
- ↑ Macnamara, J.; Derry, C. Pollution Removal Performance of Laboratory Simulations of Sydney’s Street Stormwater Biofilters. Water 2017, 9, 907. doi:10.3390/w9110907