Difference between revisions of "Planters: Sizing"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Dean Young (talk | contribs) |
Dean Young (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
If you are designing a planted system which does infiltrate water, see advice on [[Bioretention: Sizing]]. | If you are designing a planted system which does infiltrate water, see advice on [[Bioretention: Sizing]]. | ||
| − | The dimensions of a stormwater planter are largely predetermined according to the function of the component. As they do not contain a storage reservoir the planters rely more upon careful selection of materials. Both the filter media and the perforations of the | + | The dimensions of a stormwater planter are largely predetermined according to the function of the component. As they do not contain a storage reservoir the planters rely more upon careful selection of materials. Both the filter media and the perforations of the [[Pipe]] play critical roles for flow control. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Revision as of 20:22, 13 July 2020
This article is specific to flow-through stormwater planters, vegetated systems that do not infiltrate water to the native soil.
If you are designing a planted system which does infiltrate water, see advice on Bioretention: Sizing.
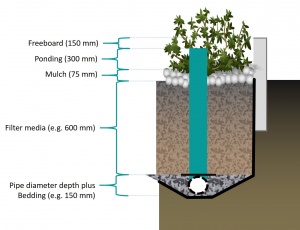
The dimensions of a stormwater planter are largely predetermined according to the function of the component. As they do not contain a storage reservoir the planters rely more upon careful selection of materials. Both the filter media and the perforations of the Pipe play critical roles for flow control.
| Component | Recommended depth (with underdrain pipe) | Typical porosity (n) |
|---|---|---|
| Ponding (dp) | ≥ 300 mm | 1 |
| Mulch | 75 ± 25 mm |
|
| filter media (dm) |
|
0.35 |
| Pipe diameter reservoir | Is equal to underdrain pipe diameter | 0.4 |
| Pipe bedding (db) | 50 mm (although commonly omitted altogether). | 0.4 |